Welcome to Virus database
The Human Virus Barcode Database (HVBD) contains six novel coronavirus variants, named Lambda, Alpha, Delta, Beta, Gamma and Omicron in chronological order of discovery.It also contains statistics on other coronaviruses known to infect humans.
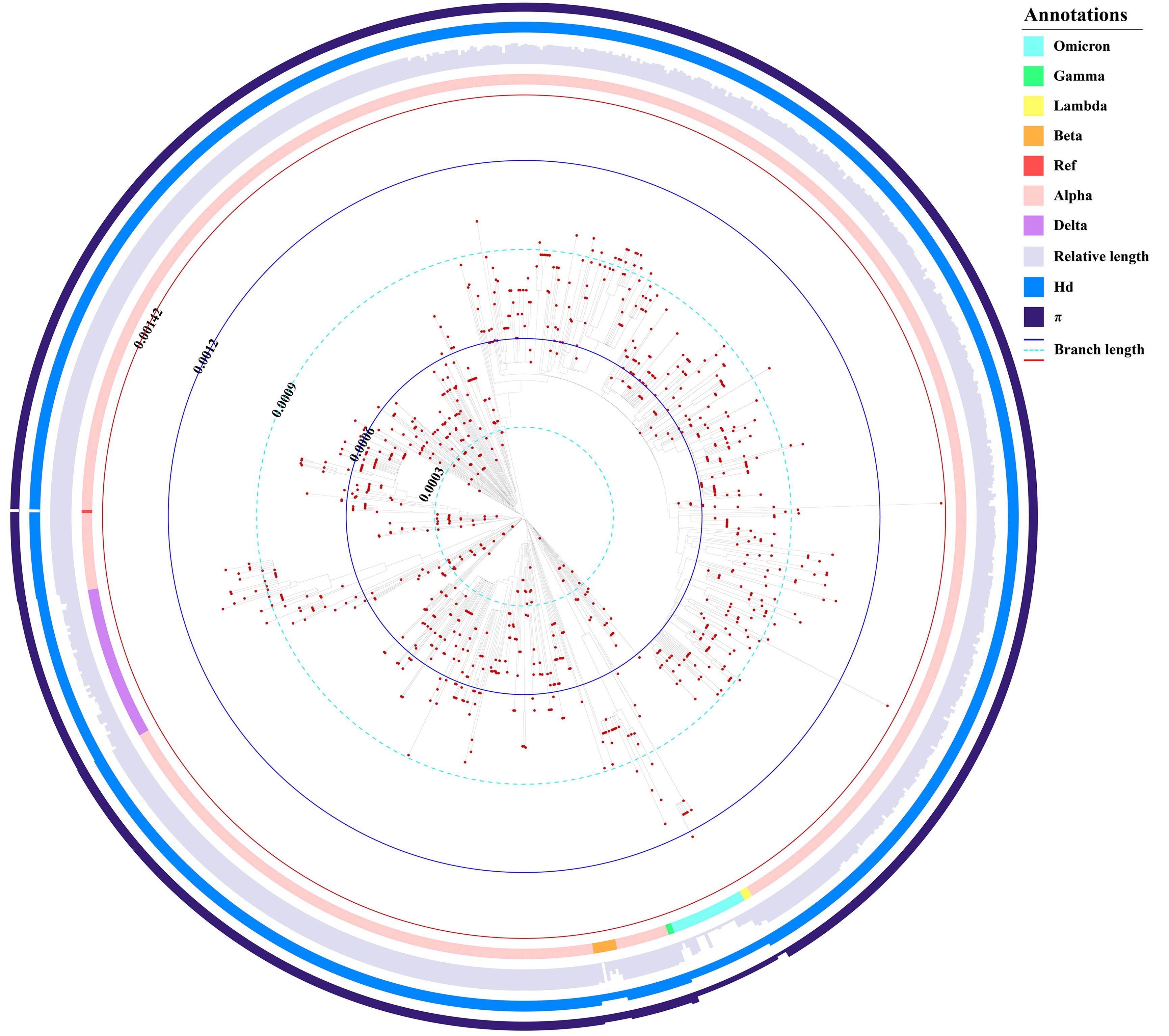
Combined barcodes of SARS-CoV-2
SARS-CoV-2, short for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, is a coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019). Belonging to the beta coronavirus genus, SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV). It is an enveloped positive-sense RNA virus with a genome of approximately 30,000 nucleotides. SARS-CoV-2 primarily spreads through respiratory droplets. Common symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection include fever, cough, difficulty breathing, fatigue, and loss of taste or smell.
Six major variants of SARS-CoV-2
Genome and Gene Annotation
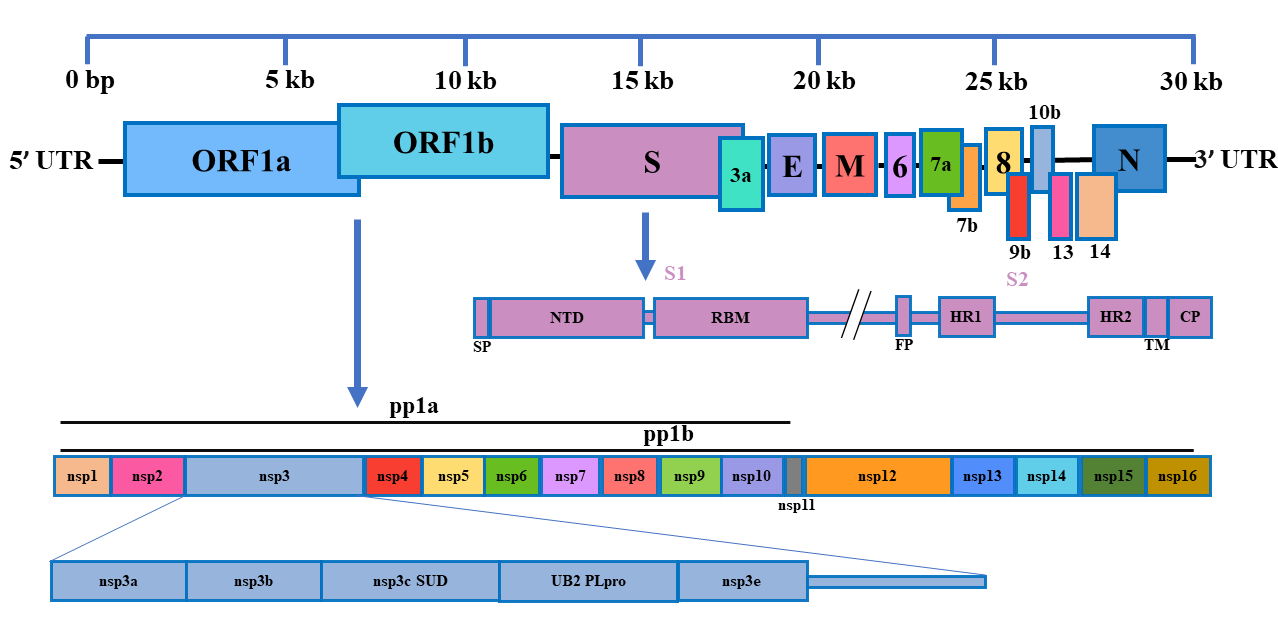
| Gene | Name | Gene function |
|---|---|---|
| ORF1ab | NSP1 | Inhibits host protein translation by the interaction with 40Sribosomal subunit and host mRNA |
| NSP2 | Disturbs cell cycle by binding to prohibitin 1 and prohibitin 2 proteins | |
| NSP3 | Interacts with host RNA G-quadruplex to inhibit host translation, suppresses host innate immune responses by deubiquitination, delSGylation, and ADPr binding | |
| ORF1ab | NSP4 | Assembling the wiral double-membrane vesicles |
| NSP5 | Protease | |
| NSP6 | Induction of autophagosomes | |
| NSP7 | Primer synthesis and RNA replication | |
| NSP8 | Primer synthesis and RNA replication | |
| ORF1ab | NSP9 | Interacts with DEAD-bOX RNA helicase 5 (DDX5) cellular protein to facilitate virus replication |
| NSP10 | mRNA cap methylation | |
| NSP12 | RNA replication, mRNA capping | |
| NSP13 | Helicase activity during RNA replication, 5'-triphosphatase activity for mRNA capping | |
| ORF1ab | NSP14 | Proof reading during RNA synthesis N7-methyltransferase during mRNA capping |
| NSP15 | Endoribonuclease cleaves RNA at polyuridylate sites | |
| NSP16 | 2'-O-ribose methyltransferase during mRNA capping | |
| S | S | Glycoproteins that mediate viral attachment to host cells |
| ORF3a | ORF3a | Induction of apoptosis |
| E | E | Small integrated membrane proteins involved in the viral replication cycle, viral assembly, virion release, and viral pathogenesis |
| M | M | Facilitate the completion of virus assembly |
| ORF6 | ORF6 | Blocking the response of infected cells to the invading virus |
| ORF6 | ORF7a | Inhibit type I IFN response |
| ORF8 | ORF8 | Blocking antigen delivery and mediating immune escape |
| N | N | nucleocapsid phosphoprotein |
Status of COVID-19
- Countries must “double-down” on their efforts to stop the spread of COVID-19 coronavirus, the UN health agency said on March 11, 2020, after announcing that the global emergency can now be described as a pandemic. UN Secretary-General António Guterres described the announcement as “a call to action–for everyone, everywhere.”
- On May 5, 2023, the head of the UN World Health Organization (WHO) has declared “with great hope” an end to COVID-19 as a public health emergency, stressing that it does not mean the disease is no longer a global threat.
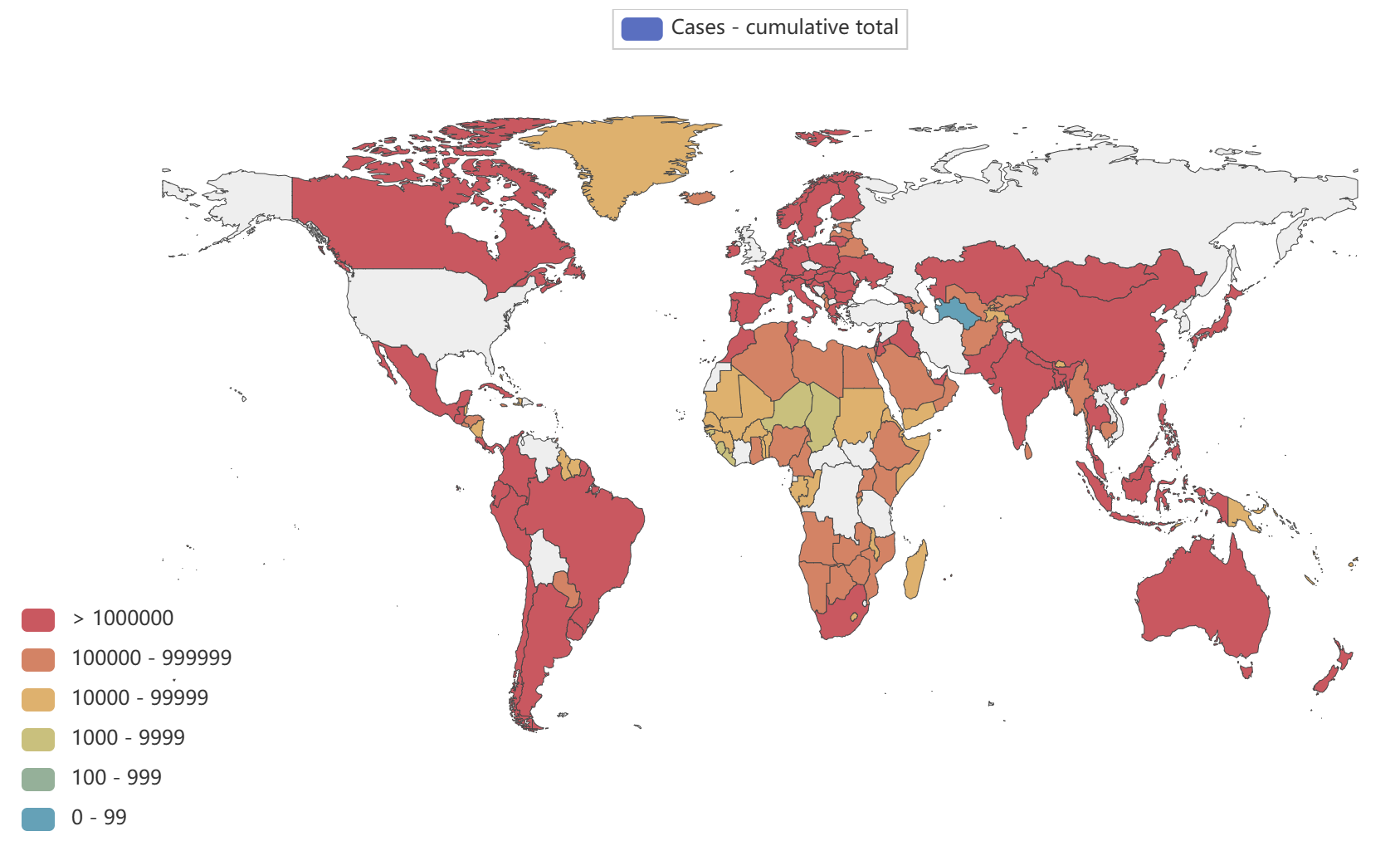
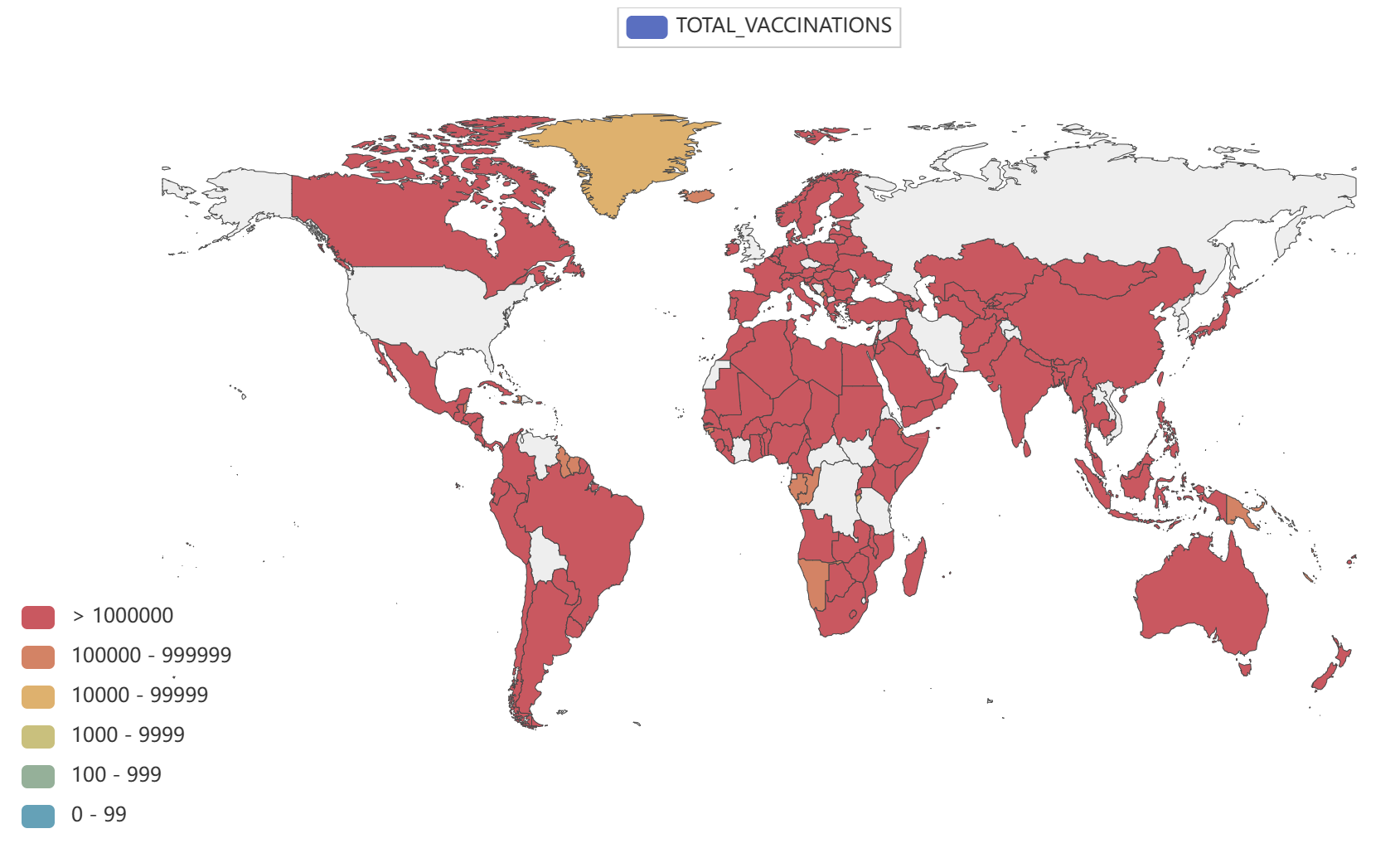
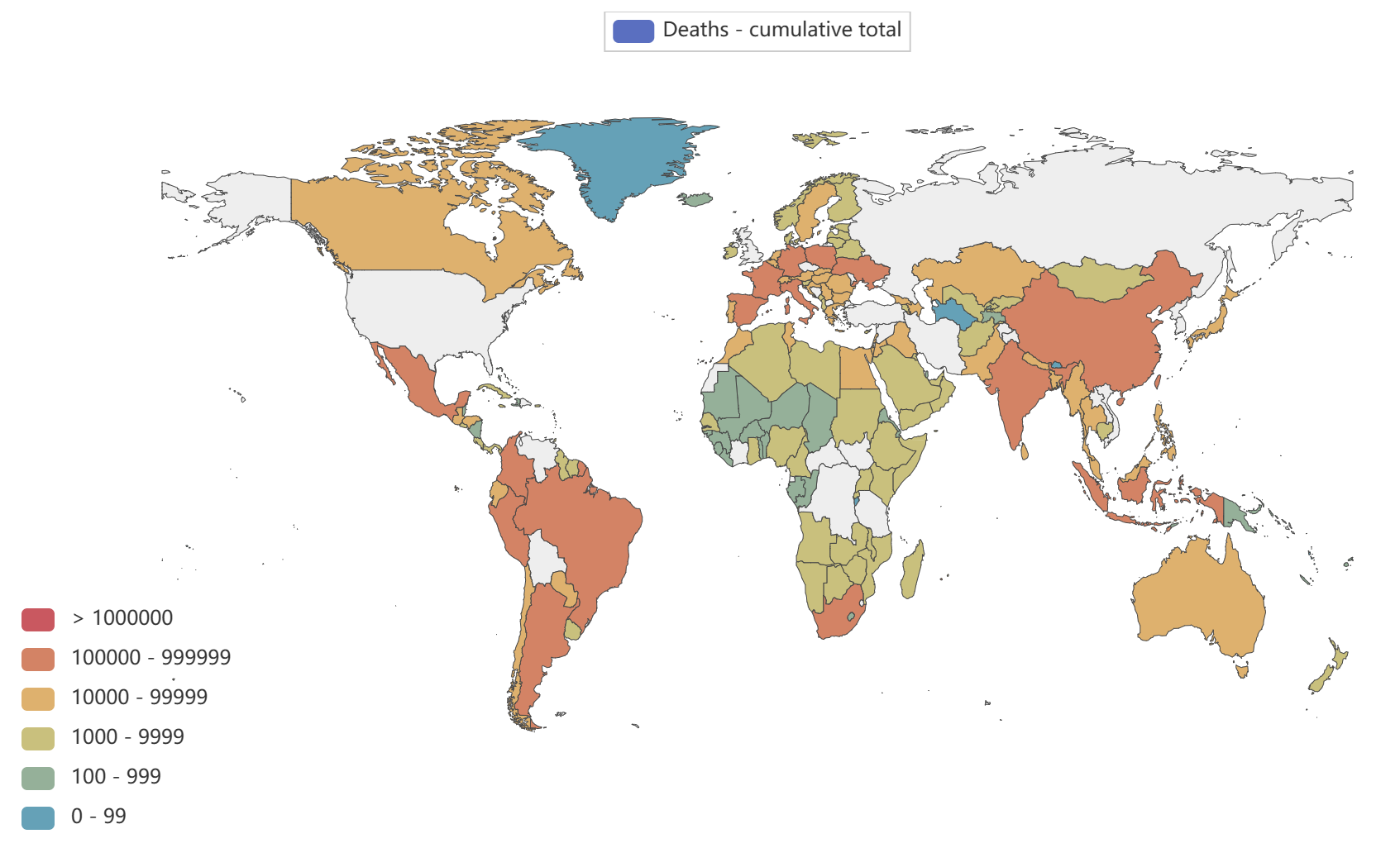
- Globally, as of 3:20pm CEST, 14 June 2023, there have been 767,984,989 confirmed cases of COVID-19, including 6,943,390 deaths, reported to WHO. As of 12 June 2023, a total of 13,397,334,282 vaccine doses have been administered.
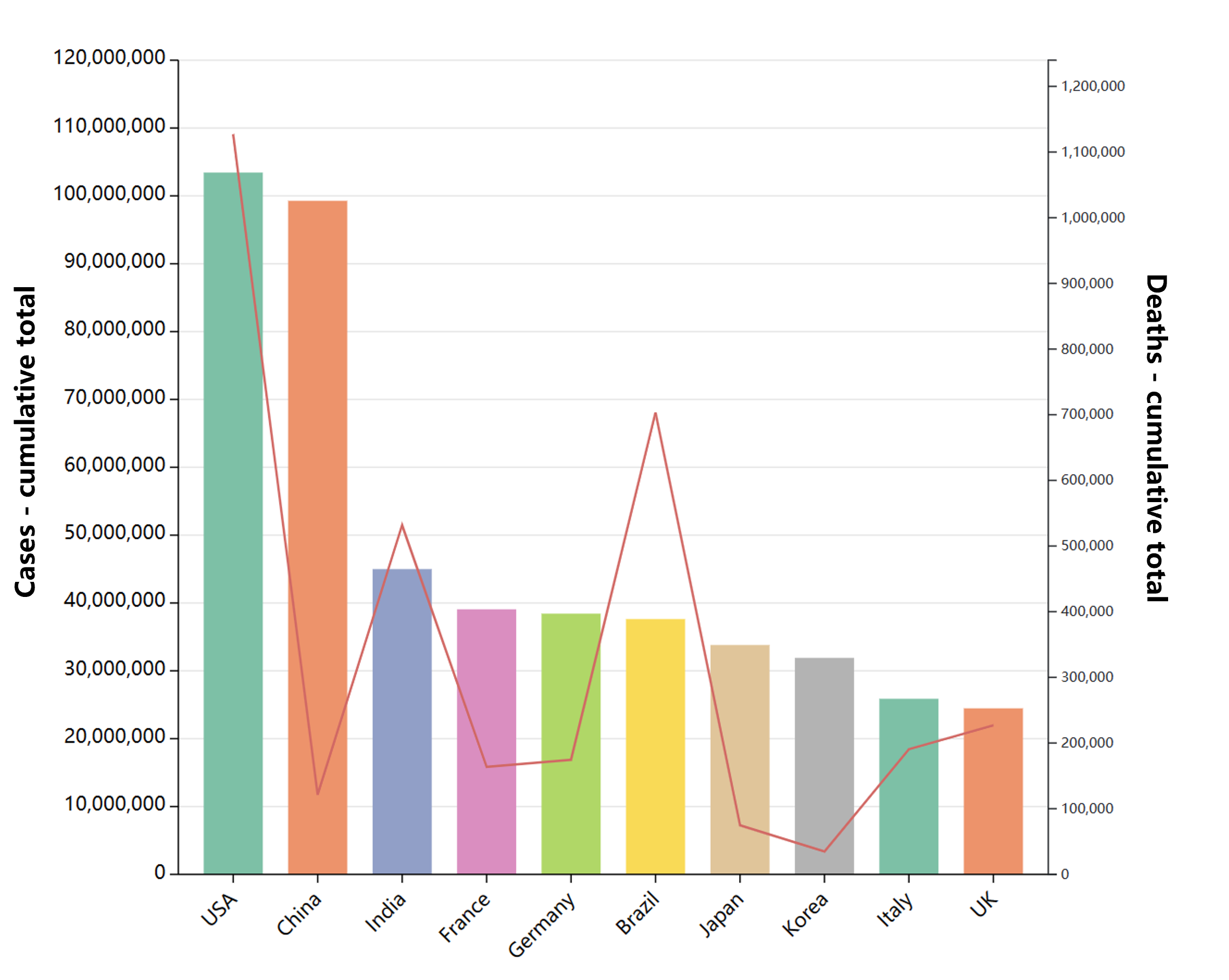
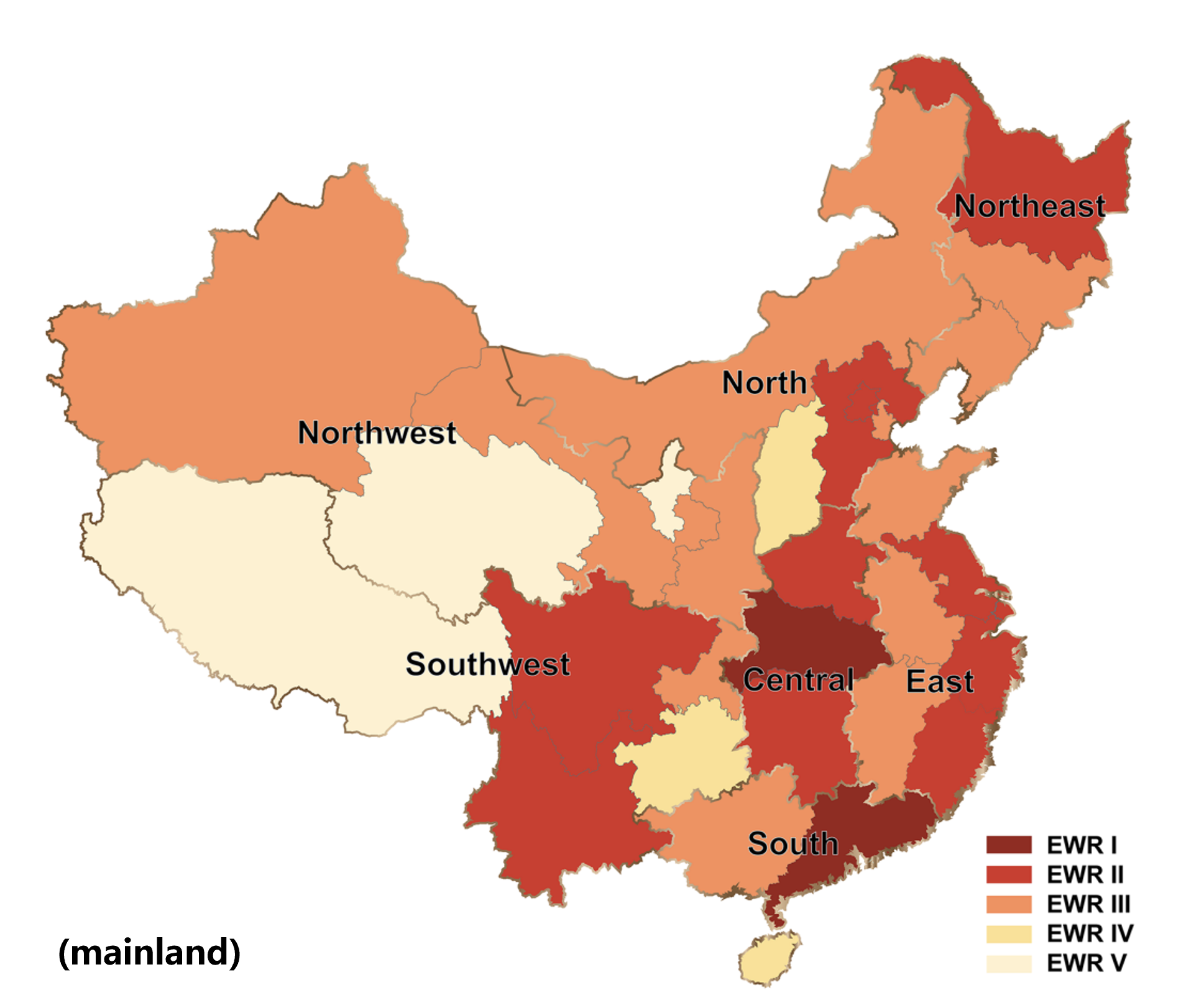
Epidemic data in China
Global epidemic data
Sequence library information

Conserved Regions
It mainly contains the conserved regions information and statistical information of each variant of the novel coronavirus.

Nucleic Acid Diversity
It mainly contains the statistical information of all known coronaviruses that can infect humans.
Resources&Tools
Literature Resources
It mainly contains virus related literature resources, which is convenient for everyone to consult.

Epidemic Informatics Analysis
The current situation and hot spots of the epidemic were analyzed based on Baidu index.



 E-mail
E-mail