Sequence Comparison Analysis
Sequence Comparison Analysis
Insthoviricetes
Pair Frequencies
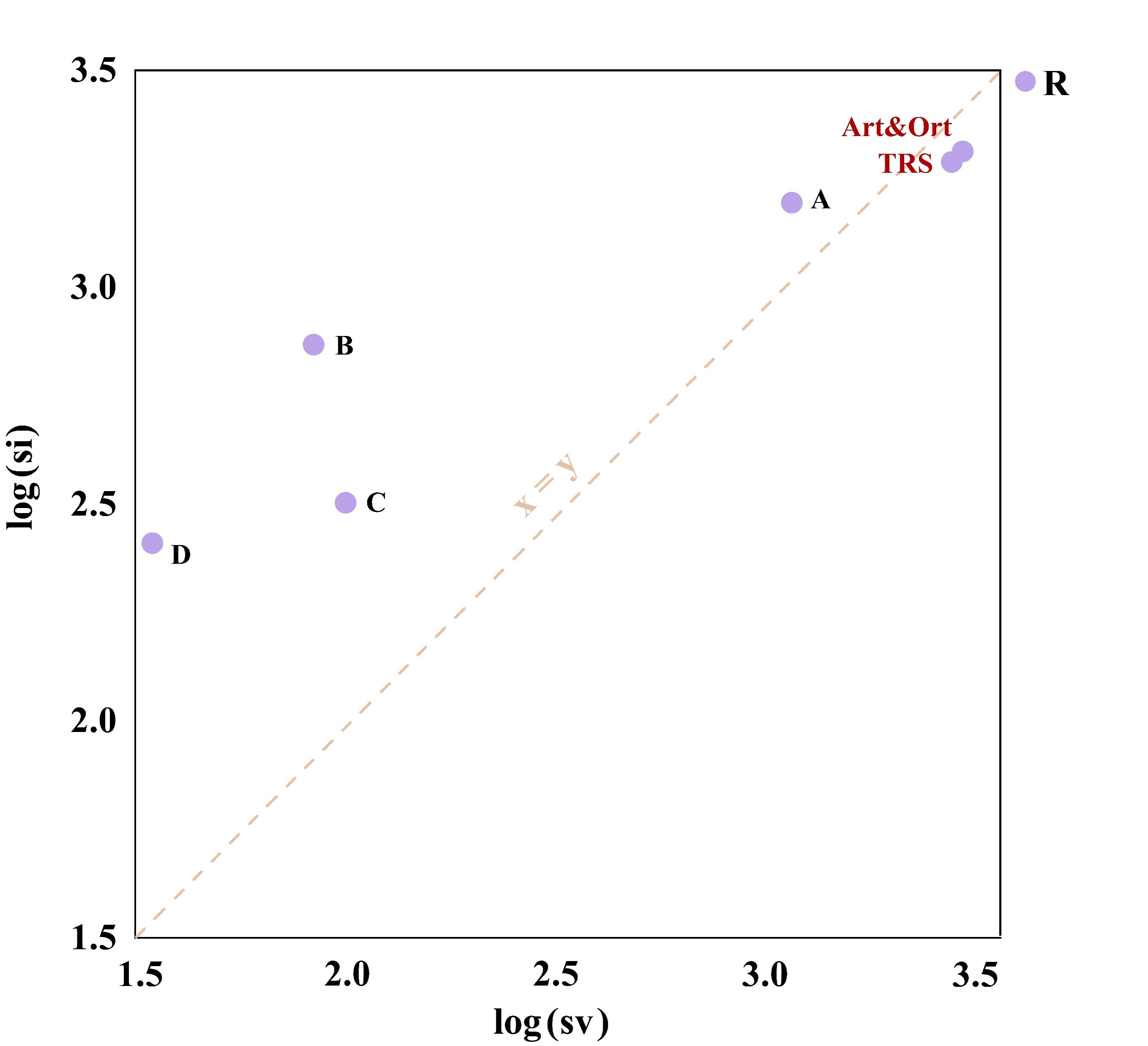
| Genera | ii (Identical Pairs) | si (Transitionsal Pairs) | sv (Transversional Pairs) | R (si/sv) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alphainfluenzavirus | 11041 | 1406 | 797 | 1.8 |
| Betainfluenzavirus | 13546 | 507 | 90 | 5.7 |
| Gammainfluenzavirus | 12237 | 315 | 120 | 2.6 |
| Deltainfluenzavirus | 12367 | 256 | 34 | 7.4 |
| Influenza virus | 7400 | 2163 | 2551 | 0.8 |
| Orthomyxoviridae | 5685 | 2192 | 2689 | 0.8 |
| Articulavirales | 5615 | 2186 | 2686 | 0.8 |
| Insthoviricetes | 5615 | 2186 | 2686 | 0.8 |
1. ii (Identical Pairs): Base pairs in DNA that are the same when two sequences are compared. They indicate the degree of similarity or genetic relationship between the sequences.
2. si (Transitional Pairs): Substitutions between purines (A and G) or between pyrimidines (C and T) in DNA. These mutations are more common because of the chemical structure similarities between purines and between pyrimidines.
3. sv (Transversional Pairs): Substitutions between a purine and a pyrimidine (e.g., A to C or T, G to C or T) in DNA. These are less common due to the more significant chemical structure changes involved.
4. R (si/sv): The ratio of transitional to transversional pairs. This ratio helps in understanding the predominance of mutation types in DNA and can indicate evolutionary pressures or repair mechanisms.
Polymorphic Sites
| Genera | Total sites | Conserved sites | Variable site | Parsim-Info sites | Singleton sites | CpG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alphainfluenzavirus | 13851 | 7814 | 5997 | 4992 | 996 | 1484 |
| Betainfluenzavirus | 14556 | 12349 | 2061 | 1741 | 320 | 3310 |
| Gammainfluenzavirus | 13868 | 11901 | 1005 | 168 | 837 | 3202 |
| Deltainfluenzavirus | 12804 | 11533 | 1267 | 730 | 537 | 3204 |
| Influenza virus | 16864 | 4074 | 12414 | 11870 | 541 | 116 |
| Orthomyxoviridae | 25853 | 1801 | 18883 | 16438 | 1940 | 0 |
| Articulavirales | 26217 | 1845 | 19373 | 16611 | 2065 | 0 |
| Insthoviricetes | 26217 | 1845 | 19373 | 16611 | 2065 | 0 |
1. Conserved Sites: DNA sequence positions that remain unchanged across different individuals or species, indicating evolutionary importance and functional significance.
2. Variable Site: Positions in DNA sequences where variations are observed when comparing different individuals or species, used to study genetic diversity.
3. Parsim-Info Sites: Sites that provide information for the least number of evolutionary changes, useful in phylogenetic construction for simplifying evolutionary assumptions.
4. Singleton Sites: Positions in a DNA sequence that show a mutation in only one individual within a population, potentially indicating recent mutation events.
5. CpG Sites: Specific DNA regions where a cytosine is followed by a guanine, often involved in gene regulation through methylation processes.
Genetic Distance
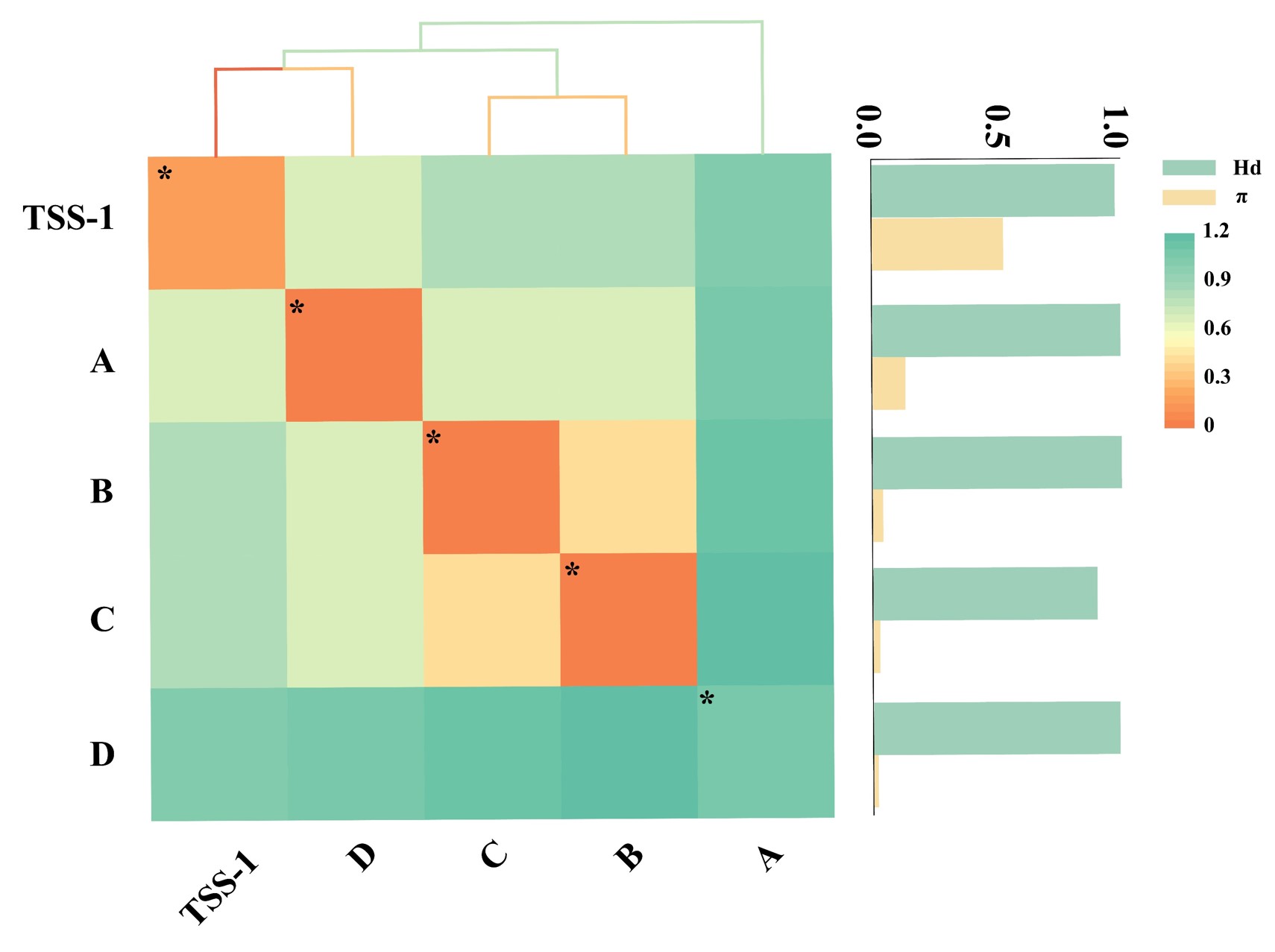
| Genera | Alphainfluenzavirus | Betainfluenzavirus | Gammainfluenzavirus | Deltainfluenzavirus | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alphainfluenzavirus | 0.152 | 0.678 | 0.803 | 0.823 | 1.035 |
| Betainfluenzavirus | 0.678 | 0.043 | 0.666 | 0.67 | 1.081 |
| Gammainfluenzavirus | 0.803 | 0.666 | 0.027 | 0.42 | 1.113 |
| Deltainfluenzavirus | 0.823 | 0.67 | 0.42 | 0.022 | 1.151 |
| Others | 1.035 | 1.081 | 1.113 | 1.151 | 1.059 |
"Others" refers to all other genera within Insthoviricetes, excluding Alphainfluenzavirus, Betainfluenzavirus, Gammainfluenzavirus, and Deltainfluenzavirus.